Psoriasis
Skin Treatments
Other Treatments
Have Any Question?
In case you wish to avail of the services from Dr. Shailesh Singh you could contact him via the following means
Request a Call Back
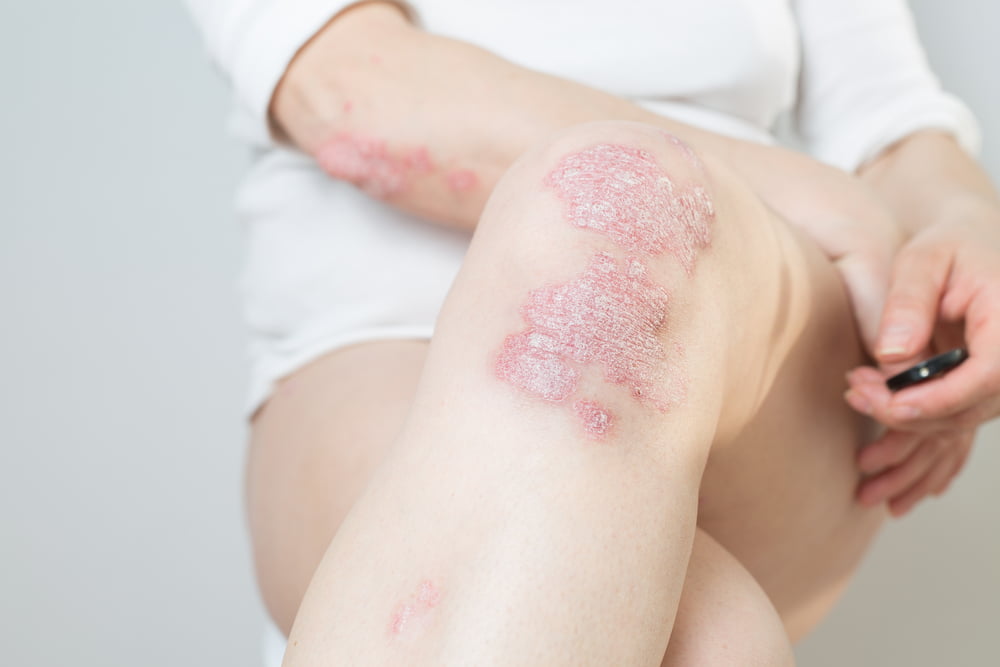
What is Psoriasis?
- Psoriasis is a common, chronic skin disease which sometimes also involves nails and joints. It affects up to 2% of the world population.
- Psoriasis is not a life-threatening disease generally but recurrences are common.
- Psoriasis is a disease which is treatable and can be effectively and completely controlled but is not curable.
How can one get psoriasis?
- The exact cause of psoriasis is not known. It is a complex interplay between genetics and immunology.
- Genetic susceptibility and environmental factors are responsible for disease.
- Normally the epidermis or outer layer of skin is continuously replaced and it takes place in three and four weeks. There is increased turnover of skin cells in psoriasis so that the skin cells are formed and shed within a week.
Is psoriasis hereditary? Is psoriasis transmissible to family members or contacts?
- Psoriasis is a multifactorial disease .
- It can be inherited, but the mechanism are complex.
- It is not necessary that children of affected parents will develop psoriasis but there is a higher chance of developing psoriasis compared to children of non-affected parents. If one parent is affected, then the chance of developing psoriasis in the child is approximately 15% and chance are increased to 40% if both parents are affected.
- Psoriasis is not an infectious disease and cannot be transmitted by contact.
What factors can aggravate psoriasis?
- Many factors are known to aggrevate psoriasis.
- Infections- sore throat and HIV infection can trigger psoriasis.
- Certain medications such as antihypertensive drugs (beta-blocker) , anti-malarial(chloroquine), pain killer, lithium and withdrawal of systemic corticosteroids can aggravate psoriasis.
- Physical trauma and mental stress can trigger psoriasis.
- Cold climates and winters commonly aggravate psoriasis in most cases, but some patients may have summer aggravation.
- Alcohol intake and smoking can aggravate the disease.
- Obesity and decreased physical activity are well known aggravating factors for psoriasis as well as other co-existing diseases with psoriasis.
What should one do if he/she gets psoriasis?
- If one gets psoriasis, he/she must consult a dermatologist.
- Don’t self medicate or take treatment from untrained physicians.
- Improper or wrong treatment may make psoriasis unstable.

