Wart
Skin Treatments
Other Treatments
Have Any Question?
In case you wish to avail of the services from Dr. Shailesh Singh you could contact him via the following means
Request a Call Back
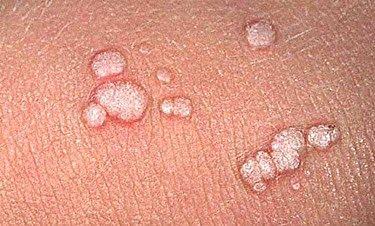
What is wart?
- A wart is a small rough growth on the skin resembling a cauliflower. Occasionally it can be smooth and plane also.
- It is caused by a virus named human papilloma virus (HPV).
How can one get warts?
- The virus usually enters the body through areas of broken skin and spreads from person to person by direct touch or by touching objects used by the infected person.
- Within the body of the affected person, it can spread from one body site to other.
- Can spread by sharing shaving kits at salons and after beauty parlor activities.
How can the infection spread? Is it transmissible to family members or contacts?
- It can spread by direct skin to skin touch or by sharing of objects and thereby can be transmitted to family members or close contacts.
- Sexual transmission can occur (genital wart).
How does the wart appear?
- Common wart: small localized swellings over the skin surface that have a roughened uneven surface and can occur anywhere including the face, hands, body and scalp.
- Flat wart: occurs as small, smooth-surfaced, skin coloured projections usually numerous in number.
- Filiform wart: appears as a slender finger like projection, usually over the face.
- Genital wart: common warts that appear over the genitals in both males anf females. However, they appear more whitish and glistening and the common warts.
- Periungual wart: a variant that occurs as a small cluster of warts with roughened cauliflower like surface around the nails.
- Plantar wart: appears as a small whitish projection on the foot with minute black dots at the centre. It is painful, particularly when present over pressure bearing areas of the sole.
- Mosaic wart: a group of tightly clustered plantar-type wart, commonly on the hands or sole of the feet.
What should one do if he/she gets warts?
One should consult a doctor qualified in treating warts i.e. a dermatologist.

